Real IELTS Examiner Techniques | Practical Structures | Personal Feedback
IELTS Line Graphs
Line Diagrams in IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
Understanding Line Graphs
Line graphs are one of the most common types of visuals in IELTS Academic Writing Task 1.
These graphs represent data points connected by lines, typically illustrating trends, changes, or patterns over a given period.
Describing line graphs accurately and coherently is essential for achieving a high band score.
This guide provides a detailed explanation of how to approach line graphs, including key strategies, structure, and vocabulary, based on a real example.
Step-by-Step Guide for Analysing and Writing About Line Graphs
Step 1: Analyse the Graph
Spend a few minutes carefully understanding the graph before writing:
-
Time Frame:
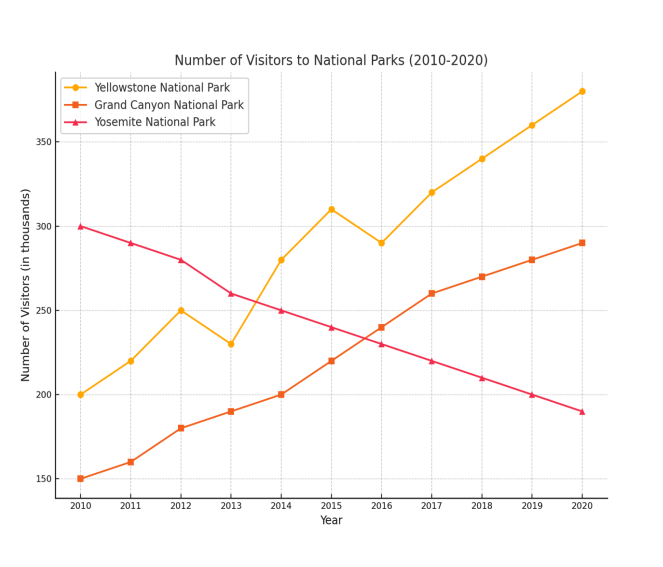
The graph covers the period from 2010 to 2020, showing trends over a decade. -
Variables:
The graph illustrates the number of visitors (in thousands) to three national parks: Yellowstone, Grand Canyon, and Yosemite. -
Trends:
-
Yellowstone: Visitor numbers fluctuated, with notable peaks and dips across the period.
-
Grand Canyon: Visitor numbers grew steadily without major fluctuations.
-
Yosemite: Visitor numbers declined consistently over the decade.
-
-
Key Data Points:
-
Yellowstone started with approximately 200,000 visitors in 2010 and peaked at around 380,000 by 2020.
-
Grand Canyon visitor numbers rose steadily from about 150,000 to 280,000.
-
Yosemite began with 300,000 visitors but declined to around 190,000 by 2020.
-
Step 2: Paraphrase the Task
Begin with a rephrased version of the task description.
-
Task Statement:
The graph below shows the number of visitors to three national parks between 2010 and 2020. -
Paraphrased Version:
The line graph illustrates the changes in the number of visitors to Yellowstone, Grand Canyon, and Yosemite National Parks over a ten-year period from 2010 to 2020.
Step 3: Write an Overview
Summarise the main trends without giving detailed data.
Overview:
Overall, the Grand Canyon experienced a steady rise in visitor numbers, while Yosemite saw a consistent decline over the period. Yellowstone’s visitor numbers fluctuated throughout the decade, showing both significant increases and decreases.
Step 4: Detailed Analysis
Organise your main paragraphs clearly:
-
Paragraph 1: Yellowstone and Yosemite
Visitor numbers at Yellowstone National Park fluctuated noticeably. Beginning at around 200,000 in 2010, the figure climbed to about 250,000 in 2012 before dipping to 230,000 in 2013. A peak occurred in 2015 at around 310,000 visitors, followed by a slight decline in 2016. Despite fluctuations, Yellowstone’s trend was generally upward, reaching approximately 380,000 visitors by 2020.
In contrast, Yosemite’s visitor numbers fell steadily from around 300,000 in 2010 to just under 190,000 by 2020, with no significant recoveries during the period. -
Paragraph 2: Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon displayed a steady and continuous increase throughout the decade. Visitor numbers rose from around 150,000 in 2010 to approximately 280,000 in 2020. Unlike the other two parks, the Grand Canyon showed no major fluctuations, making it the most stable trend among the three.
Step 5: Review and Edit
Before finishing your Task 1 response:
-
Grammar and Spelling: Check for tense consistency and grammatical errors.
-
Tense Consistency: Use past tense to describe completed periods.
-
Accuracy: Double-check that the figures and trends described match the graph exactly.
Vocabulary for Describing Line Graphs
Describing Trends:
-
Upward: increase, rise, climb, grow, surge, peak
-
Downward: decrease, decline, drop, fall, plummet
-
Stable: remain steady, level off, stabilise
-
Fluctuating: vary, oscillate, fluctuate
Adverbs for Degree of Change:
-
Large Changes: significantly, dramatically, substantially
-
Moderate Changes: gradually, steadily
-
Small Changes: slightly, minimally
Useful Linking Words:
-
To Compare: similarly, likewise, in comparison
-
To Contrast: however, in contrast, whereas
-
To Add Information: additionally, moreover
